
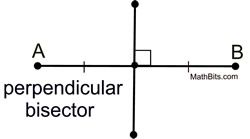
Bisector postulate definition geometry plus#
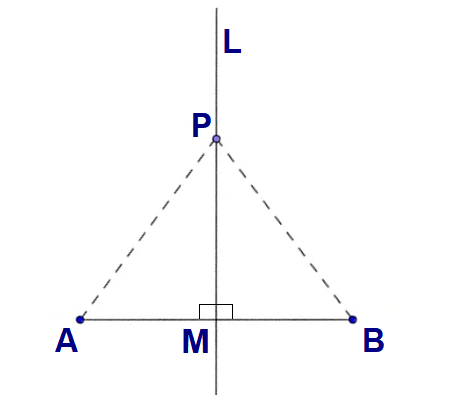
Heath's authoritative translation plus extensive historical research and detailed commentary throughout the text. The Thirteen Books of Euclid's Elements (2nd ed. 149 (original publication 1929 with Houghton Mifflin Company (Boston) as Modern Geometry). This line is known as the angle bisector.In a triangle, there are three such lines.Three angle bisectors of a triangle meet at a point called the incenter of the triangle.There are several ways to see why this is so. Posamentier: Advanced Euclidean Geometry: Excursions for Students and Teachers. The Angle Bisectors.For every angle, there exists a line that divides the angle into two equal parts.

Heath goes on to say that Augustus De Morgan proposed that the two statements should be combined as follows: If an angle of a triangle is bisected internally or externally by a straight line which cuts the opposite side or the opposite side produced, the segments of that side will have the same ratio as the other sides of the triangle and, if a side of a triangle be divided internally or externally so that its segments have the same ratio as the other sides of the triangle, the straight line drawn from the point of section to the angular point which is opposite to the first mentioned side will bisect the interior or exterior angle at that angular point. 2)), the corresponding statement for an external angle bisector was given by Robert Simson who noted that Pappus assumed this result without proof. The angle bisector theorem appears as Proposition 3 of Book VI in Euclid's Elements. | B D | | C D | = | A B | | A C |, are collinear, that is they lie on a common line. The angle bisector theorem states that the ratio of the length of the line segment BD to the length of segment CD is equal to the ratio of the length of side AB to the length of side AC: For example, an angle bisector of a 60-degree. Let the angle bisector of angle A intersect side BC at a point D between B and C. The angle bisector in geometry is the ray, line, or segment which divides a given angle into two equal parts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
